The effects of sedentary lifestyle are becoming one of the biggest health challenges of modern times. With long office hours, screen-based entertainment, and reduced physical activity, people are sitting more than ever before. This inactivity increases the risk of obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and even early death. Understanding these dangers is the first step toward building healthier habits and improving overall well-being. Let DuhoReview discover now!
Negative health effects of sedentary lifestyle on the body

Negative health effects of sedentary lifestyle on the body
The human body is designed to move, and lack of activity disrupts essential functions. When movement decreases, calories burn less efficiently, hormones change, and muscles weaken. Over time, this leads to both immediate and long-term complications.
Long-term effects of sedentary lifestyle on the body
The long-term effects of sedentary lifestyle on the body include obesity, cardiovascular disease, and metabolic disorders. Sitting too much also increases chronic inflammation and weakens the immune system. Over years, these silent changes add up to significant risks for serious diseases.
Another concern is poor circulation, which can lead to blood clots and vein-related problems. Reduced metabolism makes it harder for the body to break down fats and sugars properly. Eventually, this can trigger a chain reaction that leads to chronic conditions such as type 2 diabetes.
Effects of sedentary lifestyle on muscle loss and bone health
A sedentary routine often leads to muscle weakness and loss of endurance. Inactive muscles shrink in size, while bones lose mineral density and become fragile. This raises the likelihood of osteoporosis, fractures, and chronic joint pain.
Poor posture and long hours of slouching can also accelerate spinal degeneration. Stiff hips, weak legs, and back pain are among the most common complaints of office workers. Without strength training and regular activity, these conditions only get worse over time.
Cardiovascular and metabolic consequences
Cardiovascular and metabolic consequences
Sitting for long hours affects not only muscles but also the heart and blood vessels. Cardiovascular health suffers when circulation slows and the body cannot regulate blood sugar efficiently. Let’s look at two major consequences of physical inactivity.
Effects of sedentary lifestyle on cardiovascular health
The effects of sedentary lifestyle on cardiovascular health include increased risks of high blood pressure and heart disease. Prolonged sitting lowers cardiac output, weakens the heart muscle, and raises cholesterol levels. Even people with a normal weight are not safe if they remain inactive for long periods.
Prolonged sitting also stresses the vascular system, making arteries stiff and less flexible. Studies show that sitting more than 10 hours a day increases the likelihood of heart attack and stroke. These risks remain high even if you exercise occasionally but spend most of your day sitting.
Effects of sedentary lifestyle on diabetes risk
The effects of sedentary lifestyle on diabetes risk are well-documented in clinical studies. Prolonged inactivity reduces insulin sensitivity, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. People who sit for hours at a time are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes, regardless of body weight.
Taking short breaks throughout the day can help regulate blood sugar more effectively. Research suggests that walking for just a few minutes after meals lowers glucose spikes. This simple habit can delay or even prevent diabetes in at-risk individuals.
Weight gain, obesity, and related disorders
The effects of sedentary lifestyle on weight gain and obesity include a slower metabolism and hormonal imbalances. Inactive people burn far fewer calories, making it easier to gain fat. Over time, this leads to unhealthy weight gain and increases the risk of obesity.
Obesity from inactivity contributes to a higher risk of heart disease, diabetes, and stroke. It also leads to sleep apnea, liver problems, and reduced life expectancy. By simply adding more daily movement, weight gain can be controlled effectively.
Mental and emotional well-being
The impact of a sedentary lifestyle is not limited to the body. Inactivity also disrupts brain function and emotional health. Reduced blood flow and hormonal changes can cause mood swings and poor focus.
Psychological effects of sedentary lifestyle

Psychological effects of sedentary lifestyle
The psychological effects of sedentary lifestyle include depression, anxiety, and chronic stress. Studies reveal that people who sit for long hours are more likely to suffer from mental health disorders. This is partly due to reduced serotonin and endorphin levels in the brain.
Screen-based entertainment such as television and video games often makes matters worse. Long hours of screen time increase anxiety and disrupt sleep cycles. Without movement, the brain loses one of its most natural mood boosters: exercise.
Effects of sedentary lifestyle on mental health and productivity
The effects of sedentary lifestyle on mental health and productivity often show up as brain fog, fatigue, and lack of motivation. People who sit for long hours report difficulty concentrating on tasks. Over time, this leads to decreased work performance and reduced academic achievement.
A lack of movement also reduces creativity and problem-solving ability. Employees who spend most of their day seated are more likely to feel drained by the afternoon. Adding even short activity breaks can boost focus and energy levels throughout the day.
Physical pain and posture problems
The effects of sedentary lifestyle on back pain and posture are noticeable in both office workers and students. Sitting for long hours compresses spinal discs and weakens core muscles, leading to stiffness and lower back pain. Over time, this causes chronic discomfort that may require medical treatment.
Slouching at a desk or hunching over screens also results in rounded shoulders and neck strain. These posture issues increase the risk of herniated discs and spinal degeneration. Frequent stretching and ergonomic adjustments can reduce these harmful effects.
Cancer and hormonal-related risks
Beyond immediate physical problems, a sedentary lifestyle can influence hormone regulation and long-term cancer risk. Excess body fat, inflammation, and hormonal imbalance create the perfect conditions for disease growth. Researchers continue to link prolonged sitting with multiple forms of cancer.
Prolonged inactivity raises the risk of colon, breast, uterine, and even prostate cancers. Chronic inflammation from fat storage contributes to DNA damage, while hormone changes stimulate abnormal cell growth. These processes make cancer development more likely in inactive individuals.
Studies show that people with the highest daily sitting times have a significantly higher chance of cancer-related mortality. Screen-based sedentary behaviors, such as long hours of TV, are particularly harmful because they combine inactivity with unhealthy snacking. Maintaining daily movement can lower these risks.
Gender-specific and age-specific impacts
Not all people experience sedentary lifestyle effects in the same way. Different age groups and professions face unique challenges when it comes to inactivity. Understanding these differences helps tailor prevention strategies more effectively.
Harmful effects of sedentary lifestyle in office workers
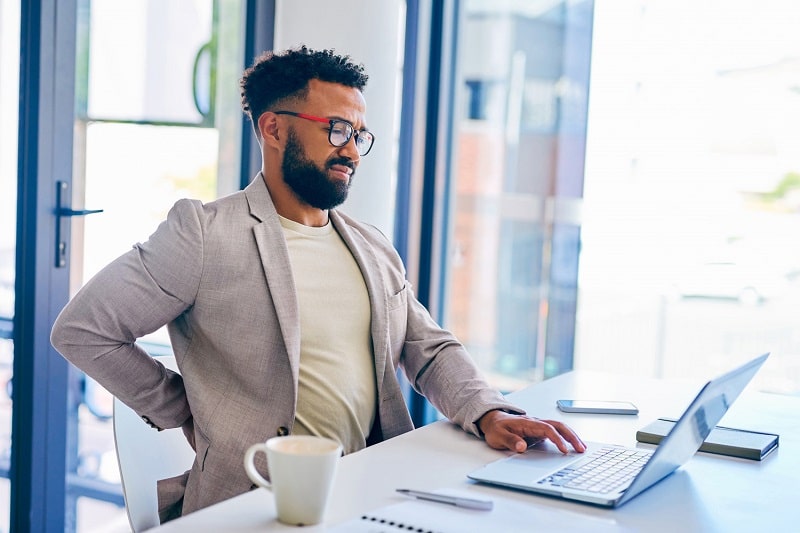

Harmful effects of sedentary lifestyle in office workers
For office workers, long sitting hours lead to poor circulation, high cholesterol, and increased blood pressure. Desk jobs often promote an unhealthy cycle of inactivity, weight gain, and stress. Over time, this combination leads to higher risks of chronic diseases.
Employees in sedentary jobs also report frequent headaches, fatigue, and eye strain from extended screen time. These factors reduce productivity and overall job satisfaction. Introducing standing desks, walking meetings, and short breaks can significantly improve workplace wellness.
Effects of sedentary lifestyle on students and young adults
Students and young adults face unique risks due to long study hours and excessive screen use. The effects of sedentary lifestyle on students and young adults include weight gain, reduced academic focus, and sleep disruption. Inactivity at a young age sets the stage for lifelong health problems.
Young people who spend too much time seated are also more prone to mental health issues. Anxiety, poor concentration, and reduced social interaction are common side effects. Encouraging physical education, outdoor activities, and regular breaks can help counteract these risks.
Sleep and reproductive health issues
Sleep quality and reproductive health are two areas strongly influenced by physical inactivity. Hormonal changes, weight gain, and circulation problems all contribute to these effects. Let’s explore how a sedentary lifestyle disrupts natural body functions.
Sedentary lifestyle and sleep disorders
A sedentary lifestyle is closely linked to insomnia and poor sleep quality. Studies show that people who exercise at least 150 minutes a week are twice as likely to enjoy restful sleep compared to inactive individuals. In contrast, nearly half of those who avoid exercise report waking up in the middle of the night.
Lack of physical activity reduces serotonin production, making it harder for the brain to regulate sleep cycles. Prolonged sitting also increases stress and anxiety, further preventing deep sleep. Adding even small amounts of daily movement can improve sleep efficiency.
Negative impact on sexual and reproductive health
Inactivity and excess weight from prolonged sitting can directly affect sexual health. Men with larger waistlines have nearly double the risk of erectile dysfunction compared to those with smaller waist sizes. Prolonged TV watching has also been linked to reduced sperm quality and lower fertility.
For women, a sedentary lifestyle may lead to hormonal imbalances that affect menstrual health and pregnancy outcomes. Weight-related issues such as obesity also reduce fertility rates and increase complications. Maintaining regular exercise helps support hormone balance and reproductive wellness.
How sedentary lifestyle affects lifespan and longevity
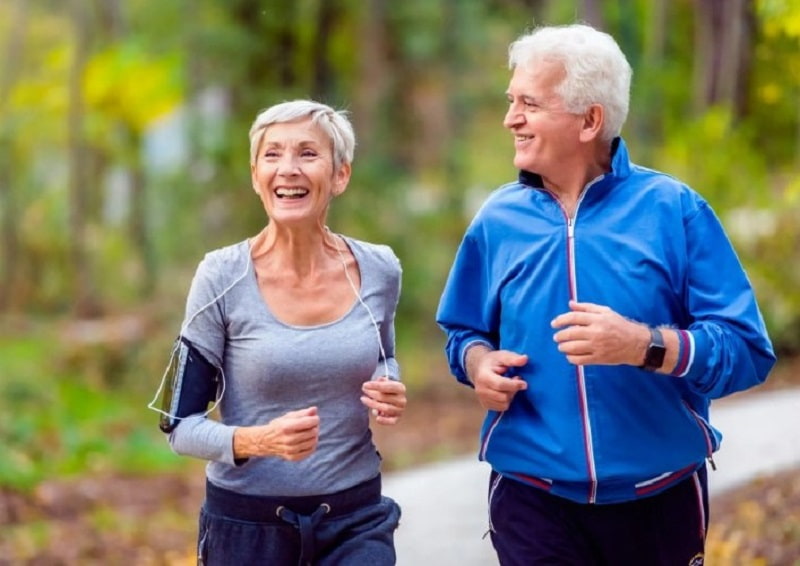

Regular exercise provides long-term benefits for both health and longevity
The ultimate cost of prolonged inactivity is a shortened life expectancy. Scientific evidence shows that sitting for more than eight hours a day raises mortality risks significantly. Even with a healthy diet, inactivity alone can increase the likelihood of premature death.
The connection between sedentary time and early death is well established in medical literature. Studies estimate that physical inactivity contributes to millions of deaths globally each year. The good news is that replacing just 30 minutes of sitting with light activity can lower the risk of early death by up to 14%.
Incorporating regular exercise into daily routines provides long-term benefits for both health and longevity. Aerobic activities such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming are highly effective at reducing mortality risks. Simply moving more throughout the day can add years to your life.
How to reverse the effects of sedentary lifestyle
The good news is that the negative outcomes of prolonged sitting can be reduced with consistent, small changes. Medical studies show that breaking up sedentary time with light or moderate activity significantly improves health markers. Let’s look at practical strategies for reversing inactivity.
Small daily changes to break sedentary habits
One of the easiest ways to counter inactivity is to add more movement into daily routines. Standing while taking phone calls, using stairs instead of elevators, or walking during lunch breaks are simple yet effective strategies. Even household chores like cleaning, gardening, or yard work can count toward daily activity.
Office workers can benefit from standing desks and “walking meetings.” Taking short breaks every 30–60 minutes reduces back pain and boosts circulation. These micro-movements, often called “exercise snacks,” may seem small but add up to meaningful health improvements.
Effective exercises to combat sedentary behavior
Experts recommend at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. Strength training twice a week is also essential to prevent muscle loss and maintain bone health. Together, these activities help offset many of the risks of inactivity.
Replacing sedentary time with structured exercise reduces risks of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer. Even light-intensity movement, such as stretching or yoga, can improve flexibility and reduce stress. The key is consistency: every bit of movement contributes to better long-term outcomes.
Frequently asked questions
The effects of sedentary lifestyle are one of the top concerns in modern health discussions. People want to know how sitting too long impacts their body and mind, and what steps they can take to reverse the damage. Below are the most common questions with clear, research-based answers.
What are the negative health effects of a sedentary lifestyle?
The negative effects of sedentary lifestyle include obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and cancer. These conditions often build up slowly and silently, becoming dangerous over time. Without change, they can reduce both quality of life and lifespan.
How does a sedentary lifestyle affect cardiovascular health?
Prolonged sitting slows circulation and increases cholesterol levels. It also raises blood pressure, which makes the heart work harder. Over years, this greatly increases risks of heart attack and stroke.
Can sitting too long cause weight gain and obesity?
Yes, inactivity lowers calorie burning and slows metabolism. Extra calories are stored as fat, particularly around the waistline. This can lead to obesity and related disorders such as sleep apnea.
How does sedentary lifestyle increase the risk of diabetes?
Long hours of inactivity reduce insulin sensitivity in the body. As a result, blood sugar levels rise more easily. This creates a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Does a sedentary lifestyle cause back pain and poor posture?
Yes, poor posture and back pain are common outcomes of long sitting hours. Core muscles weaken while spinal discs compress under constant pressure. Without stretching, these issues often become chronic.
What are the psychological effects of sedentary lifestyle on mental health?
The effects of sedentary lifestyle also extend to mental well-being. Inactivity can trigger depression, anxiety, and mood swings due to reduced serotonin and endorphin levels. Screen-based habits make these problems even worse.
How does sedentary behavior affect productivity and focus?
Sitting too long can cause fatigue, brain fog, and memory problems. Many people struggle to concentrate when they spend the entire day inactive. Short activity breaks during work hours help restore focus.
Can sedentary lifestyle cause cancer or shorten lifespan?
Yes, research confirms inactivity is linked to colon, breast, and uterine cancers. It also increases early death rates worldwide. Even small daily movements reduce these risks significantly.
What are the harmful effects of sedentary lifestyle in office workers?
Office workers often face weight gain, poor circulation, and frequent fatigue. Long sitting hours combined with high stress make these issues worse. Workplace wellness programs are key to prevention.
How does a sedentary lifestyle affect students and young adults?
Inactivity among students often results in weight gain and poor concentration. Mental health challenges like anxiety and stress are also common. Encouraging regular exercise can reverse these problems early.
Does sedentary lifestyle impact sexual health and fertility?
Yes, inactivity can lower testosterone in men and disrupt fertility in women. It also contributes to erectile dysfunction and reduced sperm quality. Active routines support hormonal balance.
How does sedentary lifestyle affect sleep quality?
Poor sleep is another hidden effect of sedentary lifestyle. Inactive people are more likely to struggle with insomnia and restless nights. Daily exercise helps regulate natural sleep cycles.
Can sedentary behavior lead to muscle loss and weaker bones?
Yes, inactivity causes muscle shrinkage and reduced bone density. This increases the chance of osteoporosis and fractures. Strength training helps restore balance and bone strength.
What are the signs that I am living a sedentary lifestyle?
Common signs include weight gain, low energy, and frequent back pain. Poor posture and difficulty concentrating are also red flags. Recognizing these symptoms early helps prevent serious health issues.
How many hours of sitting per day is considered sedentary?
Most experts agree that sitting more than six hours daily is sedentary. The most damaging effects of sedentary lifestyle appear after eight to ten hours of sitting. Standing and stretching breaks can limit harm.
Can exercise reverse the effects of a sedentary lifestyle?
Yes, regular workouts can reverse many effects of sedentary lifestyle. Aerobic activity and strength training improve circulation, metabolism, and energy levels. Starting small is enough to build long-term habits.
What are the best daily habits to reduce sedentary time?
Simple habits like walking after meals, using stairs, or standing during calls are effective. These lifestyle changes build up into major health benefits. Over time, they help prevent chronic conditions.
How much physical activity is recommended to avoid sedentary risks?
Health experts recommend at least 150 minutes of moderate activity per week. Adding two days of strength training improves results even more. This level of movement helps fight long-term health risks.
Is a sedentary lifestyle linked to early death?
Yes, one of the most serious effects of sedentary lifestyle is a higher risk of premature death. Sitting for long hours is strongly associated with reduced life expectancy. Replacing even 30 minutes of sitting with movement makes a difference.
How to stay active at work if you have a desk job?
Using standing desks, walking meetings, and short stretching breaks are practical strategies. Walking to a colleague instead of emailing is another good habit. These small changes reduce daily sitting time.
What are some simple exercises to combat sedentary behavior?
Walking, cycling, yoga, and bodyweight exercises are effective choices. These activities improve flexibility, boost metabolism, and reduce stress. Consistency is more important than intensity.
Conclusion
Prolonged sitting may seem harmless, but over time it can seriously impact your health and well-being. Building simple daily habits like walking, stretching, and exercising helps restore balance and reduce disease risks. Every step toward an active lifestyle adds strength, energy, and resilience to your body. By making these changes today, you can protect yourself from the harmful effects of sedentary lifestyle and enjoy a longer, healthier life.
Read more:
Neurozoom Reviews 2025: 35-in-1 Brain Booster for Memory, Focus & Mental Clarity
FortBite Reviews 2025: 11 Powerful Natural Ingredients for Stronger Teeth & Healthier Gums
